Purpose
The intention of this page is to present experiments with non-CRUD data operations.
Aggregation Operation
An aggregation operations adds up the values of a number of objects. When executing such an operation in RAMCloud three questions, among others, are of interest:
- Where to execute the aggregation operation (client or server side)?
- How to describe the range of objects which should be included in the operation?
- How to interpret the objects themselves?
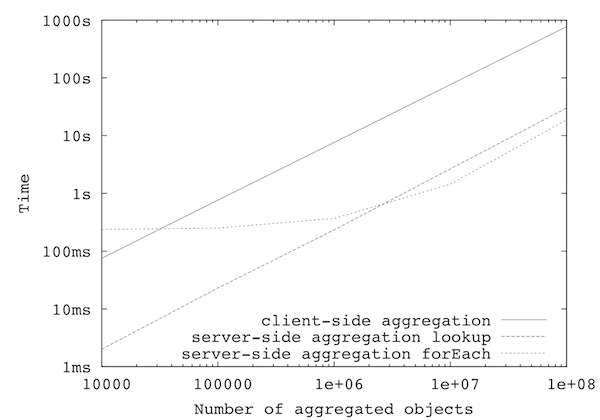
The experiments below are centered around the question about where to execute the operation. Three different scenarios are implemented:
- Client-side aggregation
Listing 1: Aggregation via looking up a certain range of keys in MasterServer.cc
for(uint64_t i = 0; i < range; ++i)
{
LogEntryHandle handle = objectMap.lookup(tableId, i);
const Object* obj = handle->userData<Object>();
int *p;
p = (int*) obj->data;
sum += (uint64_t)*p;
}
Listing 2:Aggregation using a callback in MasterServer.cc that gets invoked via objectMap.forEach()
/**
* Aggregation Callback
*/
void
aggregateCallback(LogEntryHandle handle, uint8_t type,
void *cookie)
{
const Object* obj = handle->userData<Object>();
MasterServer *server = reinterpret_cast<MasterServer*>(cookie);
int *p;
p = (int*) obj->data;
server->sum += (uint64_t)*p;
}
#number of objects |
client-side aggregation |
server-side aggregation |
server-side aggregation |
|---|---|---|---|
10.000 |
75 ms |
2 ms |
238 ms |
100.000 |
766 ms |
23 ms |
251 ms |
1.000.000 |
7604 ms |
233 ms |
369 ms |
10.000.000 |
76515 ms |
2662 ms |
1444 ms |
100.000.000 |
770761 ms |
30049 ms |
18752 ms |